1007, AARYAN WORKSPACE - 2, NR. GULBAI TEKRA, AHMEDABAD.
10AM to 7PM


Copyright is a law that gives creators exclusive rights to their original works—like books, music, and art—allowing them to control how their work is used and to earn money from it. It lasts for the creator’s lifetime plus 70 years. After this period, the work becomes public domain and can be used by anyone. Copyright encourages creativity by protecting creators’ rights and providing economic incentives.
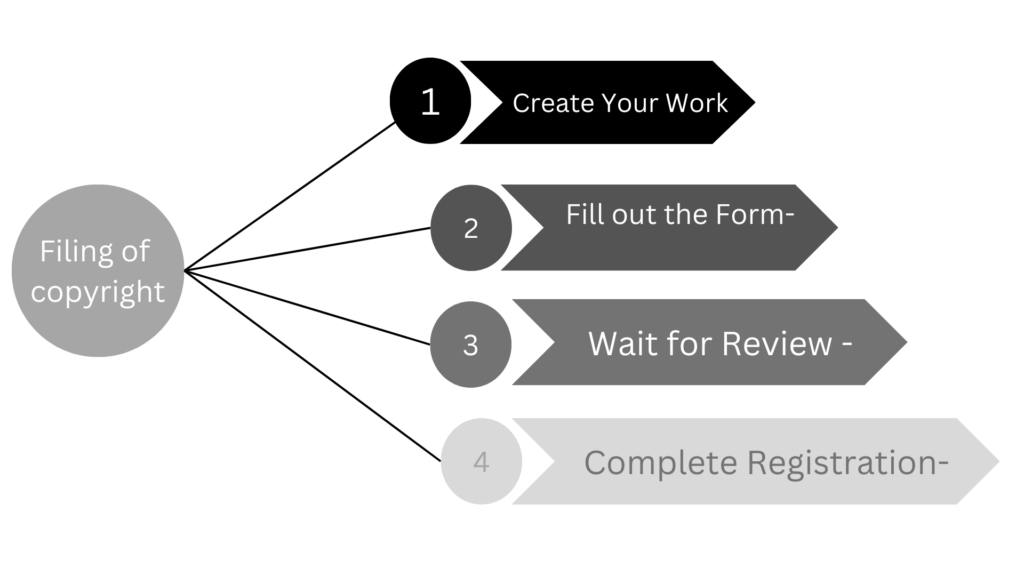
When you create something original (like a book, song, or painting), copyright protection automatically applies to it.
To complete a copyright application online, provide the applicant’s and author’s details, work specifics, and publication status. Include information on the language, nature, and title of the work, as well as details of any publications. Ensure all information is accurate and complete for proper processing.
The copyright office will review your form, which takes about 30 days. If there are any issues or questions, you might need to provide more information or clarification.
After any issues are resolved, you can finalize your registration. While you don’t need to register to have copyright, doing it can be helpful for legal protection and benefits.

-Copyright Licensing-
Copyright licensing is when the owner of a copyrighted work gives permission to someone else to use it under specific terms and conditions. This process ensures that the work can be used legally while the owner retains control and can receive compensation.
-Copyright Litigation-
Copyright litigations involve legal disputes related to the infringement or enforcement of copyright laws. These disputes can arise when someone allegedly uses copyrighted material without permission, or when there is a disagreement over the ownership or scope of copyright protection. In copyright litigation, the parties involved seek resolution through the courts, which may include determining damages, enforcing injunctions, or clarifying the rights and obligations under copyright law. The goal is to protect the intellectual property rights of creators and resolve conflicts over the use of copyrighted works.
10TH FLOOR - 1007, AARYAN WORKSPACE - 2, OPP. VASUNDHARA SOCIETY NR. PUNESHWAR FLAT, NR. GULBAI TEKRA,
Call Us For Free Consulatation
Drop Us A Mail
Navdeep & Assocciates Design & Developed by VW Themes