1007, AARYAN WORKSPACE - 2, NR. GULBAI TEKRA, AHMEDABAD.
10AM to 7PM


A trademark is a unique symbol, term, or design that identifies and distinguishes goods or services. Registering a trademark protects the brand from unauthorized use, granting the owner exclusive rights to it. This protection is crucial for maintaining brand integrity, preventing misuse, and building consumer trust.
For Example :-
3 . Protects Your Rights -: It gives you legal rights to stop other from using your brand or a similar one, helping you avoid confusion and protect your business.
5 . Adds Value -: It can increase the value of your business and be an asset that you can sell, license, or use for loans.

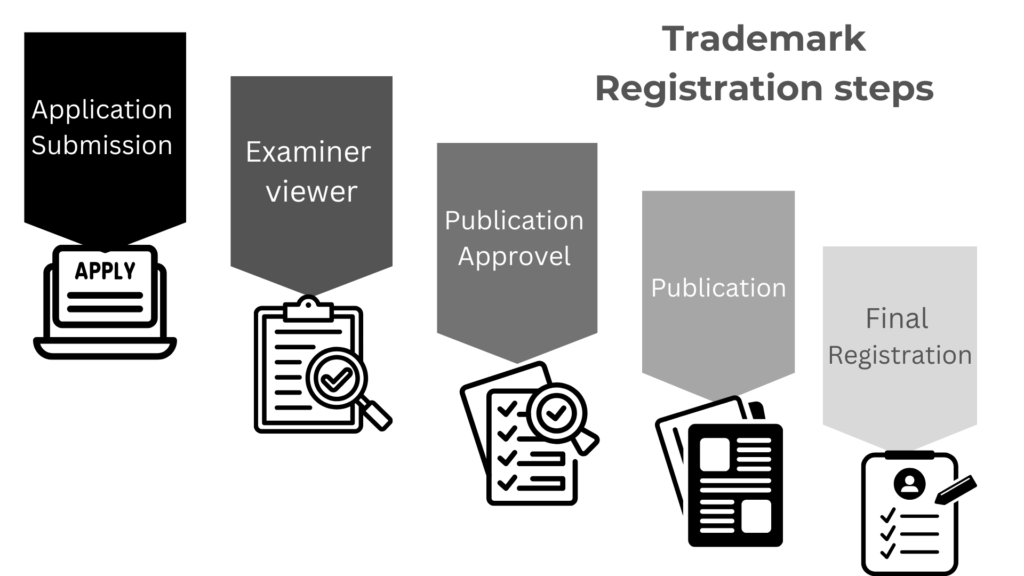
(1) – TM Application : –
Step one is to file a trademark application in the Trademark Registry India. These days, submitting is mostly done online. The application is registered, a formal receipt is immediately issued for future reference.
(2) -TM Examination : –
Following a trademark application is filed, the examiner examines it for any discrepancies. The examination could take approximately 12-18 months. The examiner may accept the trademark absolutely, conditionally or object.
(3) – Public Approval : –
An objection is one of the initial stages in the registration process. It can be submitted by either the Examiner/Registrar or some other third party. An Examiner/ Registrar can file an objection under Section(s) 9 (Total Grounds of Refusal) and 11.
Section 9 objections are created while the Registrar/Examiner considers the trademark to be descriptive of goods , generic , laudatory , quality or character of products.
Section 11 objections are made by the Registrar/Examiner whenever there’s an identical/similar trade mark in regard to identical/similar goods/services on record from the Trade Mark Registry. In such cases, the Registrar/Examiner issues a computer created Search Report using the listing of conflicting marks.
(4) : – Publication : –
Trademark journal publication is an important step in the registration of a trademark. In case a trademark program hasn’t been objected by the Trademark Examiner in the examination report or when there was an instance, and it had been defeat, then the mark will be printed in the trademark journal.
(5) : – Final Registration : –
When the program continues for trademark registration, following publication in Trademark Journal, a registration certificate under the seal of the Trademark Office is issued.
10TH FLOOR - 1007, AARYAN WORKSPACE - 2, OPP. VASUNDHARA SOCIETY NR. PUNESHWAR FLAT, NR. GULBAI TEKRA,
Call Us For Free Consulatation
Drop Us A Mail
Navdeep & Assocciates Design & Developed by VW Themes